Sports Nutrition FAQ by Aman Puri, Founder, Steadfast Nutrition
Sports Nutrition is the study and implementation of a diet or plan designed to enhance athletic performance. Nutrition plays an important role in maximizing energy and aiding sports recovery. It consists of a variety of foods (proteins, carbohydrates, fats, fiber, and more), fluids, and nutrients.
While it is important for everyone to eat and drink in the right balance, the level of nutrients required by strength and endurance sports athletes differs from those required by non-athletes. An athlete's diet may require more calories, and individuals training for bodybuilding competitions will need more protein, so a good nutrition plan is essential.
Decoding sports nutrition with Aman Puri, Founder of Steadfast Nutrition
Steadfast Nutrition is a premium sports and wellness nutrition brand introduced to offer high-quality supplements to professional athletes and fitness enthusiasts. Its parent company, Steadfast Medishield, is a trailblazer in the field of renal care, with many life-saving medicines to its credit.
It is this experience that drives the company's "We understand organs better" slogan. The company aims to revolutionize the world of sports and wellness nutrition in India by following a unique vision to serve people of all age groups. Steadfast Nutrition ensures that it uses premium grade ingredients, and dutifully adheres to ICMR, FSSAI, and WHO guidelines to ensure that its products are steroid and heavy-metal free.
In an exclusive chat about sports nutrition, Sportskeeda caught up with Aman Puri, the founder of Steadfast Nutrition.
Q. As good nutrition becomes more accessible to the average person and not just athletes, what tips do you have for a commoner on how to maintain a healthy diet?
A: A healthy diet is always balanced, consisting of micro and macronutrients. A healthy diet is also about eating at the right time. When both conditions are met, it leads to a healthy physical self. These days, nutritional products and information are widely available and easily accessible. India has taken giant strides in the nutraceutical industry segment; various companies offer nutritional supplements for wellness and well-being.
Currently, the Indian diet is protein-deficient. Therefore, adding protein to the diet is very important. Protein intake should happen through supplementation, especially in the case of vegetarians. HerbFast is an excellent solution for protein intake. Keeping your electrolytes balanced and regular fluid intake will help in various ways.
Regular consumption of water keeps the body temperature regulated and increases the efficiency of the kidneys' filtration process. Therefore, having enough water during the day is highly recommended for a healthy lifestyle. A healthy diet involves eating varied foods, including protein in every big meal, and minimizing the use of processed foods.
Q. Many people believe that supplements are harmful. What is your take on this topic and how can supplements benefit a person?
A: Excess usage of anything is harmful. Always take supplements from companies that have a better reputation and are research-focused. Supplements are not harmful when taken properly and at the right time. They are more beneficial for one’s body as they lead to better bodily functions and organ vitality.
There is also a stereotype that supplements are steroids. This is not true as proper supplementation can reduce many health problems and improve the quality of life. In the case of athletes, supplements can improve performance, leading to medal-winning performances, which bring glory to the country.
Q. Since protein is crucial for the building, maintenance, and repair of body tissues, and the basic Indian diet lacks protein, what suggestions would you give to Indians to increase the amount of protein they consume?
A: A majority of the Indians are vegetarian. Even non-vegetarians do not consume enough protein every day. 73 percent of Indians are deficient in protein, and more than 90 percent are unaware of their daily protein requirements. The recommended dietary allowance for protein given by the Indian Council for Medical Research is 0.83 gm per kg of body weight. Yes, the Indian diet indeed lacks protein, which leads to various health issues and an under muscular-skeletal structure, which also reduces organ functioning to a great extent.

Having regular and optimal protein intake leads to increased strength, improved immunity, and an active lifestyle. This will also lead to a disease-free life. The best form of protein is either whey protein or egg protein. It’s necessary to include protein as a supplement in your diet because getting enough protein from food becomes difficult for an average person.

Athletes, in particular, require more protein for better muscular strength and performance. However, this should not exceed more than 1.5- 2g/kg/day. Steadfast has the vision to make India protein-efficient by 2040. We’ve launched a variety of protein supplements to meet people’s needs. From athletes and fitness enthusiasts to people with a sedentary lifestyle, Steadfast has protein formations that meet varied requirements.
Q. Macro counting is important for athletes, but should common people also track their macros?
A: Keeping a balance of micro and macronutrients is very important for everyone. Macronutrients include carbohydrates, fat, and protein. One should not exceed the ratio of 60 percent carbohydrates, 30 percent protein, and 10 percent fat in their daily diet. The requirements of these essential nutrients vary with age, gender, physiological status, and physical activity, and can be altered by a nutritionist.
If one follows an exercise regime, keeping an account of the macros helps in keeping one’s weight in control. It also strengthens bones and muscles, boosts energy, and increases the ability to do daily activities.
Q. What is the best way to lose or gain weight by using nutrition? Can you explain calorie surplus and calorie deficit in more detail?
A: Plan your diet to minimize the risk of inadequate intake of nutrients. One way to achieve this with certainty is to use RDA as a guide. There is no single regimen for weight reduction - weight loss plans have to be gradual and customized according to an individual’s needs.
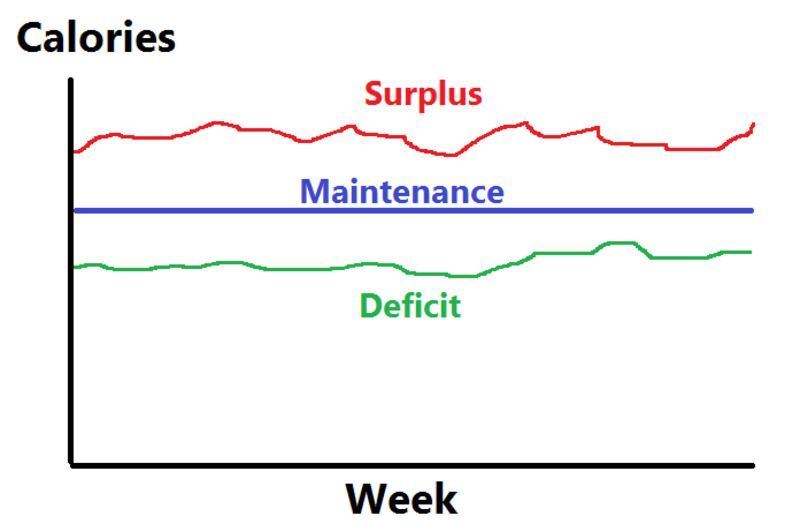
If one has to lose or gain weight, intake of calories does matter. A calorie deficit diet is for weight loss - one has to eat and drink fewer calories than they can burn. If you take in more than calories than you burn, then you don't have a calorie deficit and you won't lose weight. Physical activity and changing what and how much you eat are the only ways in which you can raise your calorie deficit.
Q. How do you feel about sugar and the various artificial sweeteners that have invaded the market in recent years as alternatives to sugar? How safe are they really?
A: Sugar is always better than artificial sweeteners, but with the advancement in research and new formulations available in the market, artificial sweeteners are offering better relative sweetness than sugar, and without calories. Even if we compare calorie counts, the benefit is that those who want to go on a calorie-deficit diet can consume artificial sweeteners to get a sweet taste but not to gain weight or improve.
The downside is that whenever we consume anything that has a sweet taste, the body understands that sugar is being ingested and the brain signals the pancreas to release insulin. Excessive consumption of artificial sweeteners will thus lead to a regular release of insulin in the body.
Q. Are carbohydrates a misunderstood vigilante or an evil villain? Could you shed some light on carbohydrates and the rumors surrounding them?
A: Carbohydrates are not villains. They fulfill the body's basic requirements and are vital for brain and organ functioning. 60 percent of our food intake should be in the form of carbohydrates. Low carbohydrate intake can cause side effects like brain fog, wherein the brain’s ability to make decisions reduces drastically. It also impacts one’s mood and behavior. The recommendation is to include complex and not simple carbohydrates in one’s diet.
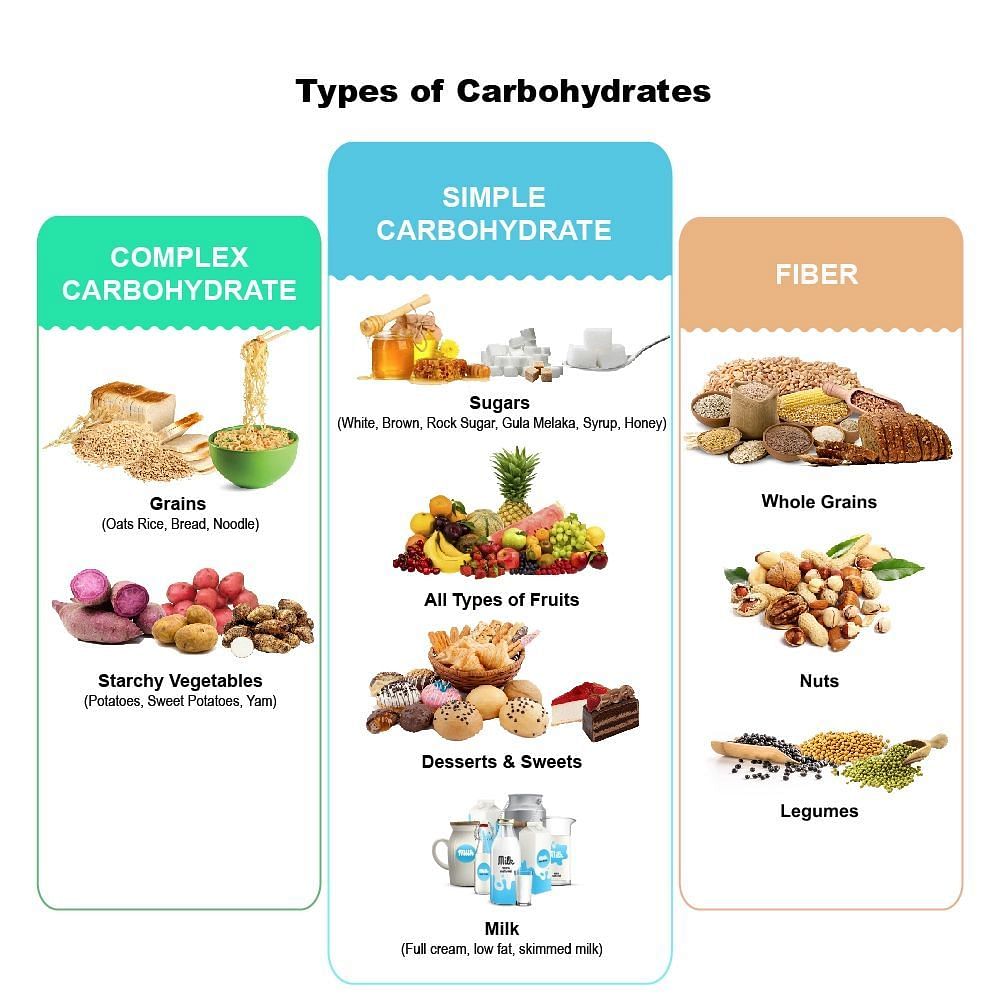
Complex carbohydrates will have a low glycemic index and could lead to stable glucose levels in the body. Complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, vegetables, and fruits are also rich in fiber, essential vitamins and minerals, which provide us with adequate nutrition.
On the other hand, simple carbohydrates such as refined flour and sugar are also known as “bad carbohydrates” because they are high in calories and devoid of essential nutrients. A high intake of simple carbohydrates can lead to many metabolic disorders.
Q. Macronutrients are ranked higher when it comes to importance. Why are micronutrients so important?
A: Yes, macronutrients should indeed be taken in higher quantities and one should keep a balanced intake of all the macronutrients. Carbohydrates (major source of energy) are the most important and should be taken most abundantly, followed by protein (building blocks of every living cell) and fat (concentrated energy source).
One should understand that the body functions with both macro and micronutrients. Micronutrients include all the essential vitamins and minerals that help in organ vitality and organ function. A deficiency of micronutrients can cause an electrolyte imbalance in the body, leading to organ failure. Hence, it’s important to maintain a balance between micro and macronutrients.
Q. In order to recover properly after exercising, what should one eat and which foods must they avoid?
A: After exercising, it’s important to have a high protein diet as the muscles have gone through wear and tear and require immediate repair. Proteins help in the synthesis and recovery of muscles. Pairing protein with carbohydrates helps in keeping the metabolism and energy level of the body optimal.

Q. Body fat and dietary fat are vastly different, and people often confuse them. Why is fat important, how does it benefit you, and where is it found?
A: Body fat is the accumulation of excessive calories. Fat that is not used by the body for energy generation, or is not metabolized by the body, gets stored in the body as fat. Dietary fat is the intake of fat through food - it can include medium and long-chain triglycerides, which can be both saturated and unsaturated. Foods that are high in fat include butter, cheese, peanut butter, and even red meat.
Ghee from milk is also a good source of fat as it improves the functioning of the body and lubricates the joints. It also improves cholesterol level and is considered a good fat since it improves the overall lipid profile of the body.
Olive Oil is also considered a good fat. Monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA) and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) are good fats. MUFA reduces bad cholesterol, and PUFA is indispensable as it cannot be synthesized by humans and is mainly present in plant foods. Vegetable oils, pulses, mustard, fenugreek seeds, green leafy vegetables, and fish are all good sources of PUFA.